The equation for the transmission of an ideal etalon, an Airy Function, is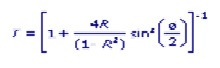
where
T = transmission
R = reflectivity of the mirrors
Φ = the roundtrip phase change of the light ray
If any phase change at the mirror surfaces is ignored, then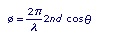
where
λ = the wavelength of the light
n = the index of refraction of the material between the mirrors
d = the distance between the mirrors
q = the angle of the incoming light beam
The above figure plots the etalon spectral transmission. The distance between adjacent peaks is the Free Spectral Range (D), and the width (FWHM) of each peak is the resolution (d). The Free Spectral Range can be written three ways: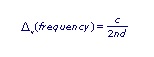
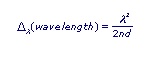
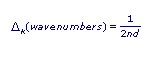
Another useful concept for etalons is finesse (F). This dimensionless parameter is the ratio of the free spectral range to the peak width.
For an ideal etalon, only the mirror reflectivity determines the finesse.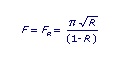
Imperfections in the etalon, such as not-perfect flatness and parallelism, will degrade the finesse. TecOptics Corp. includes the various imperfections into our etalon design calculations, so we guarantee all quoted specifications.
© 2021 TecOptics Corp. All rights reserved. Website by web.com.